Publications /
Policy Brief
This publication was originally published in the IEMed Mediterranean Yearbook 2022
The informal sector plays a major role in most MENA economies. It employs a large share of the total population and, on average, accounts for about 22% of GDP. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), which defines informal employment as the proportion of workers without access to social security, the share of informal employment in total employment in MENA countries ranges from 45% in Jordan to 80% in Morocco, with intermediate values of 59% in Tunisia, 63% percent in Egypt, 67% in Iraq and 70% in Syria.
In all MENA countries, informal employment is most prevalent in the agricultural sector, followed by industry and the services sector. The prevalence of informality in total employment in the agricultural sector ranges from 69% in Jordan to almost the entire workforce in countries including Yemen, Egypt and Syria. In industry, informal employment ranges from 57% to 83%, and in the services sector, from 38% to 73% (Chart1).
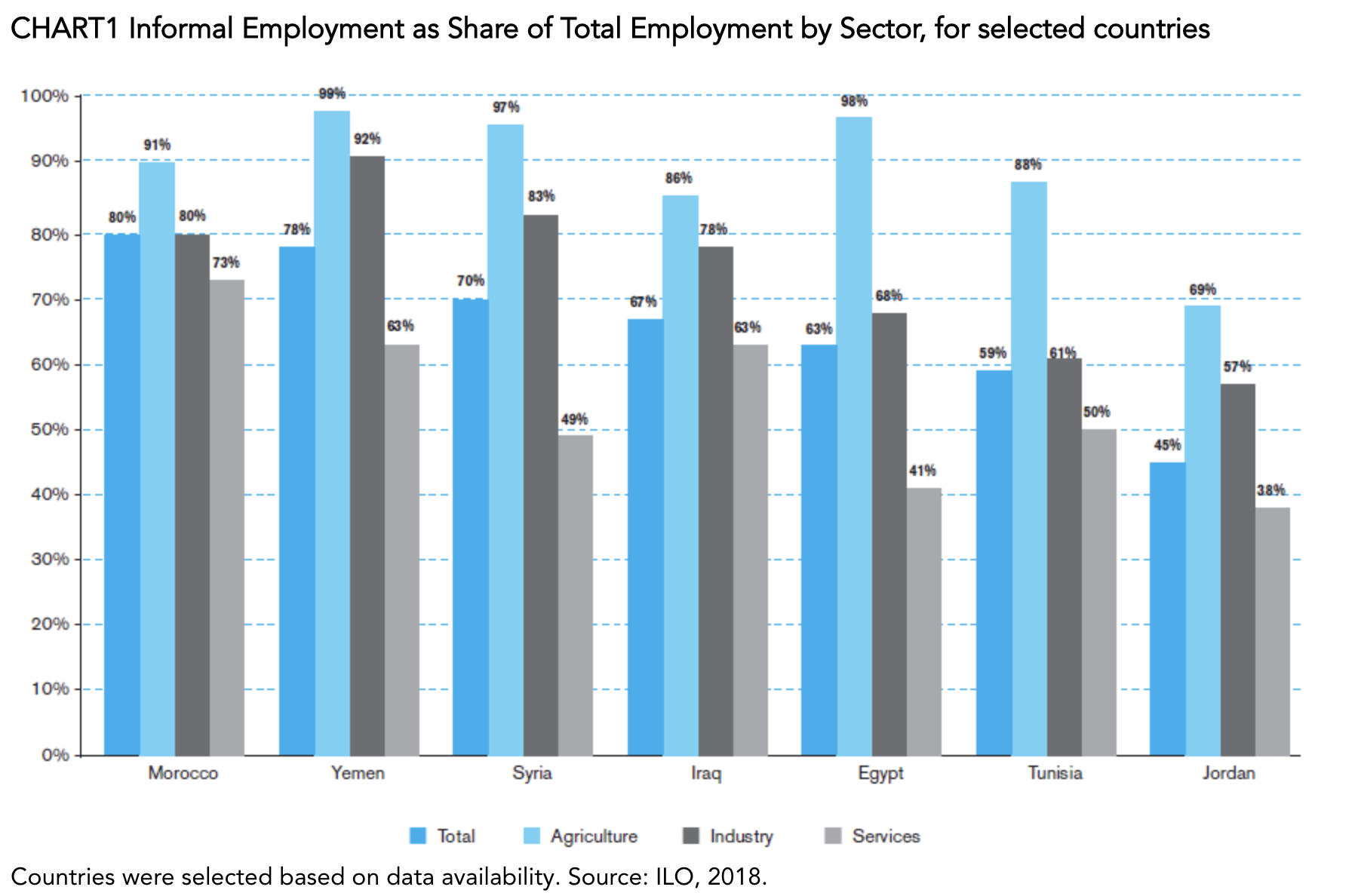
The Informal Sector Is the Main Social Safety Net for a Large Proportion of Workers in the MENA Region
The informal sector’s large share, both in terms of GDP and job creation, has several advantages and disadvantages. First, the informal sector provides a social safety net for a large part of the population in these countries, especially for new entrants to the labour market who are unable to find jobs in the formal sector, particularly low-skilled workers. The informal sector helps by filling some of the common labour market shortages in MENA countries, which are characterized by high unemployment rates, especially among young people and women, which comprise nearly 27% of the total labour force, and by the inability to create enough formal jobs to absorb the stock of workers and new labour market entrants.
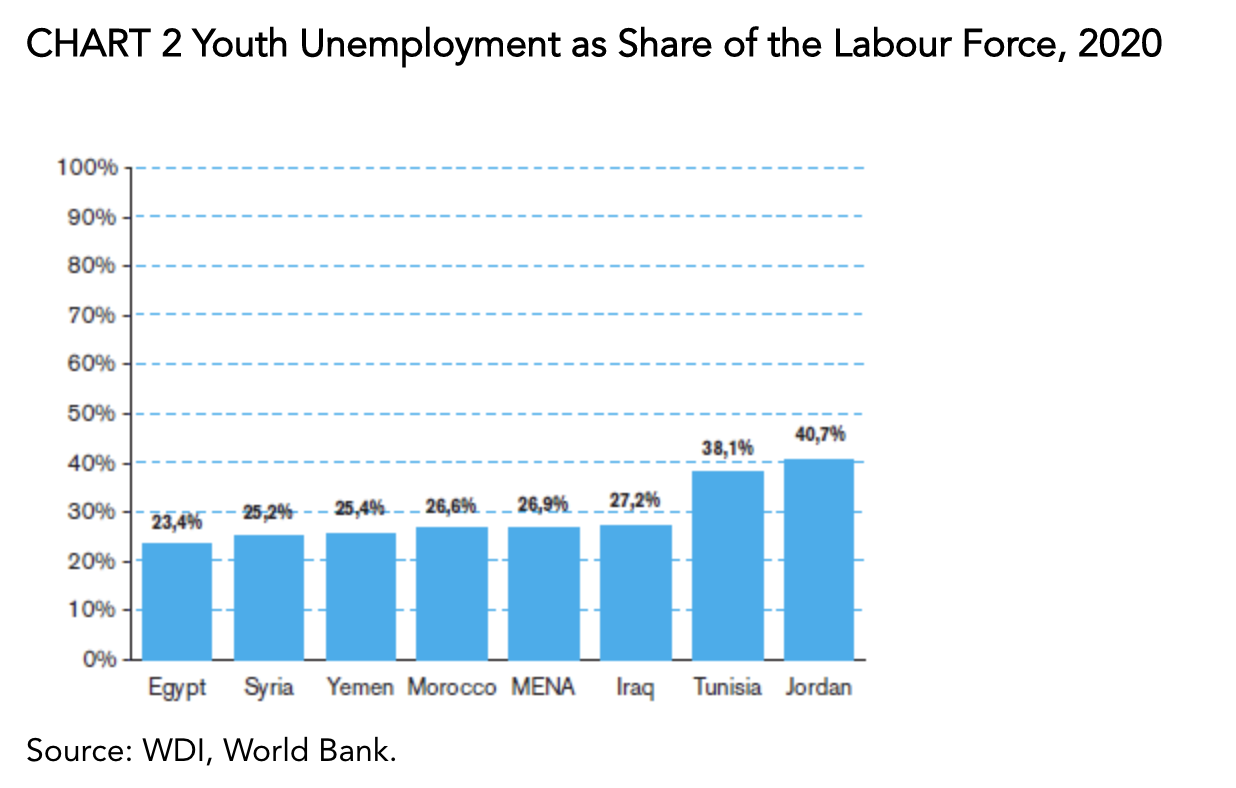
In addition, the informal sector absorbs some of the workers who are forced to turn to the informal sector, or even to leave the formal sector, in times of crisis. As a result, the sector acts as a shock absorber during economic crises and, in the absence of automatic economic stabilizers such as unemployment insurance or job loss compensation, acts as a social safety net in these countries (Saoudi, 2019).
But the Informal Sector Is Also a Source of Vulnerability for a Number of Workers
However, a large share of this sector in the economy is also a source of vulnerability for a large part of the population in these countries. High levels of informal employment mean that most of the population in these countries are not well protected by social security systems, and do not benefit from basic work-related rights, such as compulsory health insurance, unemployment insurance or job loss compensation, family allowances, pension entitlements, or work accident and disability insurance. It should be highlighted that almost 37% of the total population in the MENA region has no social protection at all, while 42.4% benefit from social assistance programmes. Only 15.2% of the population is covered by more than one social protection programme. The biggest challenge that policymakers face in implementing effective programmes of this nature remains the absence of a statistical system to help target the vulnerable and the poor.
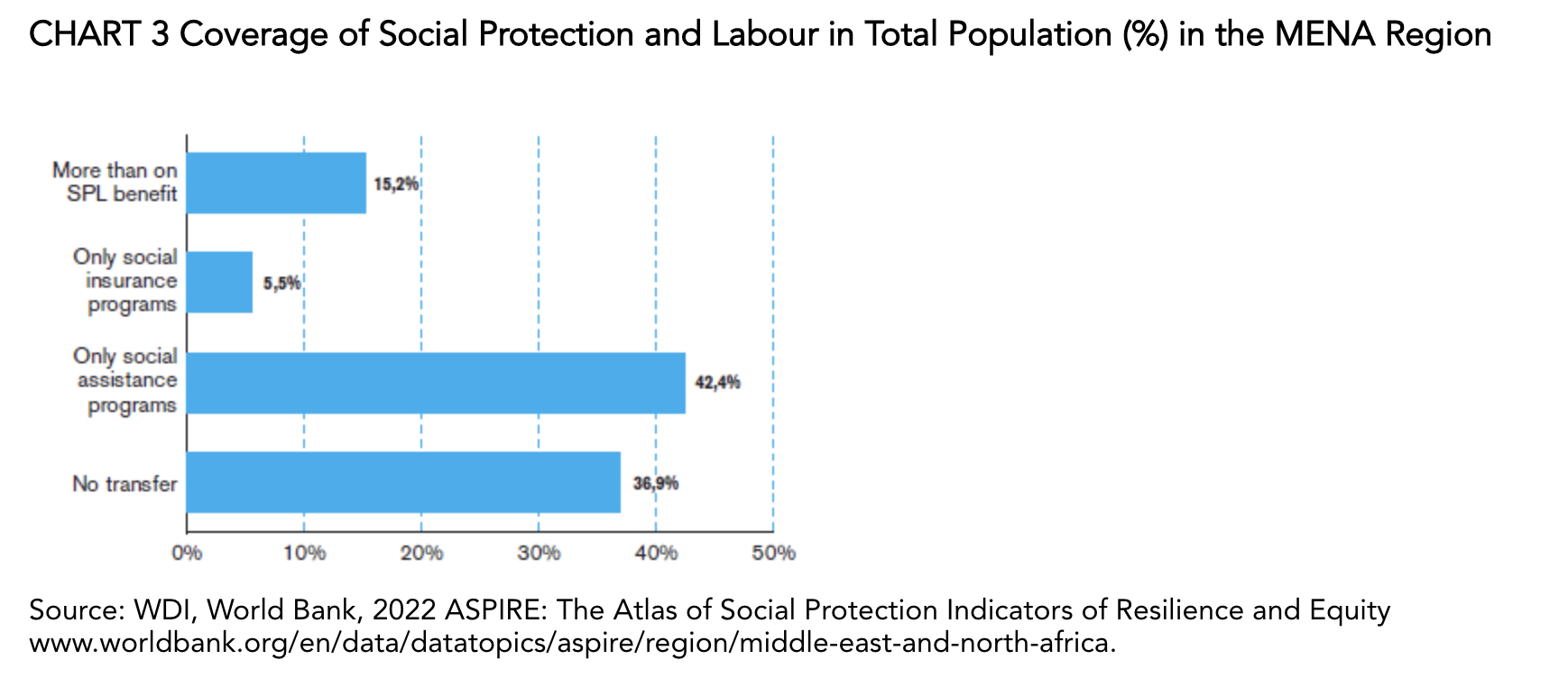
The Lack of Vocational Training and Poor Working Conditions in the Informal Sector Limit the Long-Term Prospects for Career Development and Social Mobility for a Large Proportion of these Workers
Although the informal sector helps to address certain labour market shortages in several countries in the region and provides a short-term solution to unemployment, especially for young people and women who cannot find formal jobs, in the long term it limits career development opportunities and social mobility for a large proportion of these workers. Given the lack of vocational training, and poor working conditions that do not promote skills development for workers in this sector, it remains difficult to improve conditions for workers in this sector.
Furthermore, the prevalence of a large informal sector leads not only to an additional loss and deterioration of the informal workers’ skills, but also sends a poor-quality signal regarding the skills of those workers to recruiters in the formal sector, and limits the informal workers’s prospects of joining the formal sector, for which these workers lack the minimum qualifications.
Because of unfavourable working conditions, the level of quality-of-life satisfaction for a large proportion of MENA workers, especially those in the informal sector, is steadily deteriorating. This was already the case long before the Covid-19 pandemic. In 11 of the 14 MENA countries for which data is available, quality-of-life satisfaction in 2019 was lower than in 2010 (Hoogeveen & Lopez-Acevedo, 2021).
The Informal Sector Was Hit Hardest by the Covid-19 Pandemic
The coronavirus crisis has highlighted the importance for policymakers to find a way out of the informal sector. In previous economic and financial crises, the informal sector acted as a shock absorber and social safety net for many workers, but in this pandemic a large majority of informal workers found themselves, overnight, without any source of funding to meet their minimum consumption needs.
Moreover, while containment, curfew and social distancing measures undoubtedly saved lives, they also penalized economic activity and had a disproportionate impact on informal-sector workers (IMF, 2021). Many informal-sector workers were faced with the dilemma of either starving to death or dying from the virus. The ILO estimated that of the world’s 2 billion informal workers, nearly 1.5 billion were significantly affected by social containment and distancing measures adopted by governments in 2020. Most of these workers were in Asia-Pacific and Africa, where there are nearly 988 million and 325 million informal workers respectively.
Moreover, the Covid-19 shock led to a sharp decline in the median monthly income of informal workers, and a significant increase in relative poverty, especially among informal workers, including in African and MENA countries (ILO,2020).
The Combination of Governments’ Limited Room for Manoeuvr and Very High Levels of Informal Employment May Lead to Instability and Social Tensions in Some Countries in the Region in the Medium and Long Term
The Covid-19 crisis was marked by a strong return of the state in several MENA countries, with intense recovery policies, both to avoid the collapse of the economy and to protect the most vulnerable, especially informal workers. Indeed, 21 MENA countries[1] have taken measures to cope with the effects of the crisis by setting up targeted cash-transfer programmes for those hit hardest by the crisis.
In general, these programmes have not been aimed directly at informal workers. However, some countries, such as Morocco, took advantage of high nationwide mobile phone penetration and established a unified internet portal to better tailor the delivery of targeted cash transfer programmes to assist workers who had lost their jobs. These interventions, as important and necessary as they are, may not be sustainable in the long run if countries face further crises over a long period, given the limited fiscal space available in many MENA countries. The Covid-19 crisis has highlighted the fact that the combination of a limited fiscal space and a large share of informal workers -highly prone to economic shocks- can further increase the risk of social tensions.
It is also worth noting that the Russian-Ukrainian conflict poses a new challenge to MENA economies that rely on imported commodities, including gas, oil and wheat. The prolongation of this conflict, accompanied by new sanctions against Russia, increases concerns about food supply and security, and may further increase inflationary pressures that will disproportionately impact low-income workers and ultimately lead to the risk of social unrest in some MENA countries.
Low-income informal workers will be particularly hard hit by the general increase in prices caused by the conflict. A prolonged Russia-Ukraine conflict will make recovery even more difficult and will increase the challenges for MENA governments, which face tighter budgets and difficult spending and policy choices.
Conclusion and Policy Recommendations
The economic environment is increasingly uncertain. Current uncertainties are the Covid-19 crisis and the crisis related to the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. The future will see other shocks, both climate-related and technological, which could lead to major displacements of labour and further negatively affect informal workers (Saoudi, 2021). However, the present context also provides a great opportunity for MENA countries to implement inclusive policies to foster the gradual transition of informal workers and enterprises into the formal sector.
Governments should pursue a balanced strategy to formalize the informal sector. The focus should be on both increasing the productivity of the informal sector, and encouraging the expansion of formal enterprises by developing flexible fiscal, regulatory and legal frameworks that are conducive to private-sector development and formal-sector job creation. Policies should also identify and remove barriers that may discourage or impede the formalization of informal enterprises. Governments should put in place mechanisms to strengthen the capacity of tax administrations to control and combat tax evasion.
Reforms should also aim to make the formal sector more attractive, including by improving the business climate, facilitating access to finance and public procurement for small businesses, and also by building more flexible, resilient and inclusive social protection systems. Universal social protection for all workers, including those in the informal sector, is a priority for MENA countries to help workers prepare for possible future crises, and to facilitate the upcoming technological transition, which will be accompanied by a number of disruptions to the labour market (Saoudi, 2021). The big challenge for MENA governments is to ensure the sustainability and durability of the financing of this social protection system. Governments must implement reforms aimed at creating more fiscal space, through; i) boosting economic growth and removing barriers to the participation of women in the labour market, ii) broadening the tax base by implementing a more progressive tax policy, and iii) rationalizing and coordinating all government spending by eliminating and replacing non-targeted food and energy subsidy programmes with targeted social safety nets and transfers. Underpinning this, there is a need to improve access to data and to establish a dynamic statistical tool that can be used to identify the poor and the vulnerable, who are most likely to need and to benefit from social assistance programmes.
References
Saoudi, Hamza. “Les cycles économiques ont-ils un effet asymétrique sur le chômage et la pauvreté ? Cas du Maroc.” Research papers & Policy papers 1902, Policy Center for the New South, 2019.
Saoudi, Hamza. The impact of new technologies on employment and the workforce: What are the implications for developing countries, especially in Africa? Policy report. Policy Center for the New South, 2021. Available at: www.policycenter.ma/publications/impact-new-technologies-employment-and-workforce-what-are-implications-developing
ILO (International labour Organization). Women and Men in the Informal Economy: A Statistical Picture, Geneva: ILO, 2018. www.ilo.org/global/publications/books/WCMS_626831/lang–en/index.htm,
ILO. Impact of lockdown measures on the informal economy, ILO brief, Geneva: ILO, 2020. https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/employment-promotion/informal economy/publications/WCMS_743523/lang–en/index.htm
ILO The impact of COVID-19 on the informal economy in Africa and the related policy responses, ILO brief, Geneva: ILO, 2020. www.ilo.org/africa/information-resources/publications/WCMS_741864/lang–en/index.htm
IMF (International Monetary Fund). Regional Economic Outlook, A fragile recovery continues in the Middle East and Central Asia region, 2018. Available at www.imf.org/en/Publications/REO/MECA/Issues/2021/10/14/regional-economic-outlook-october
Hoogeveen, Johannes G.; Lopez-Acevedo, Gladys. Répercussions et répartition des effets de la pandémie de COVID-19 dans la région Moyen-Orient et Afrique du Nord, World Bank, 2021. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/36618/211776ovFR.pdf










