Publications /
Opinion
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the name given to the broad spectrum of technologies by which machines can perceive, interpret, learn, and act by imitating human cognitive abilities.
Automation was created to better fulfill repetitive tasks, increasing productivity. AI, with its impressive rate of evolution, can produce new content: texts, images, new computational codes, possibly medical diagnoses, interpretations of data, and so on. It is no coincidence that an AI-based technological revolution is predicted.
I like the way Jesús Fernández-Villaverde of the University of Pennsylvania illustrates the differences between automation and AI:
“Artificial intelligence is not designing a robot that will put a screw in a car on a production line when the time comes, but designing a robot that knows how to interpret that the car arrived crooked to the left or that the screw is broken, and that will be able to react sensibly to this unexpected situation.”
AI will have consequences in areas beyond the economy, including national security, politics, and culture. In the economy, it promises to reshape many professional functions, as well as the division of labor, and the relationship between workers and physical capital. While the impact of automation has been on repetitive work, the impact of AI tends to be on tasks performed by skilled labor.
What effect will AI have on productivity and economic growth, and on social inclusion and income distribution? The impact on work processes and the labor market will be a key element in answering these questions.
It can be anticipated that, in segments of the work process where human supervision of AI will continue to be necessary, the trend will be a substantial increase in productivity and demand for work. In other segments, AI could lead to significant displacements or the simple elimination of jobs. As Daron Acemoglu and Simon Johnson put it in an article in the December edition of the International Monetary Fund’s Finance and Development magazine, “to support shared prosperity, AI needs to complement workers, not replace them”.
The systematic increase in aggregate productivity could, in principle, reinforce economic growth and, thus, underpin increases in aggregate demand, generating employment opportunities that would compensate for the destruction of jobs. This evolution could also lead to the emergence of new sectors and professional functions, while others disappear, in a dynamic that will go beyond mere intersectoral reallocation.
In addition to the effects on employment and wage-income distribution, income distribution will also depend on the impact of AI on capital income. This will tend to grow in activities that create and leverage AI technologies or have stakes in AI-driven industries. Depending on the implications in terms of the ‘market power’ of firms, there will be effects on the distributions of capital income and between capital and labor.
On January 14, the IMF released the results of exploratory research into the impacts of AI on the future of work . An estimated 60% of jobs in advanced economies will be affected, with the percentage falling to 40% in emerging economies, and 26% in low-income countries, because of differences in their current employment structures (Figure 1).
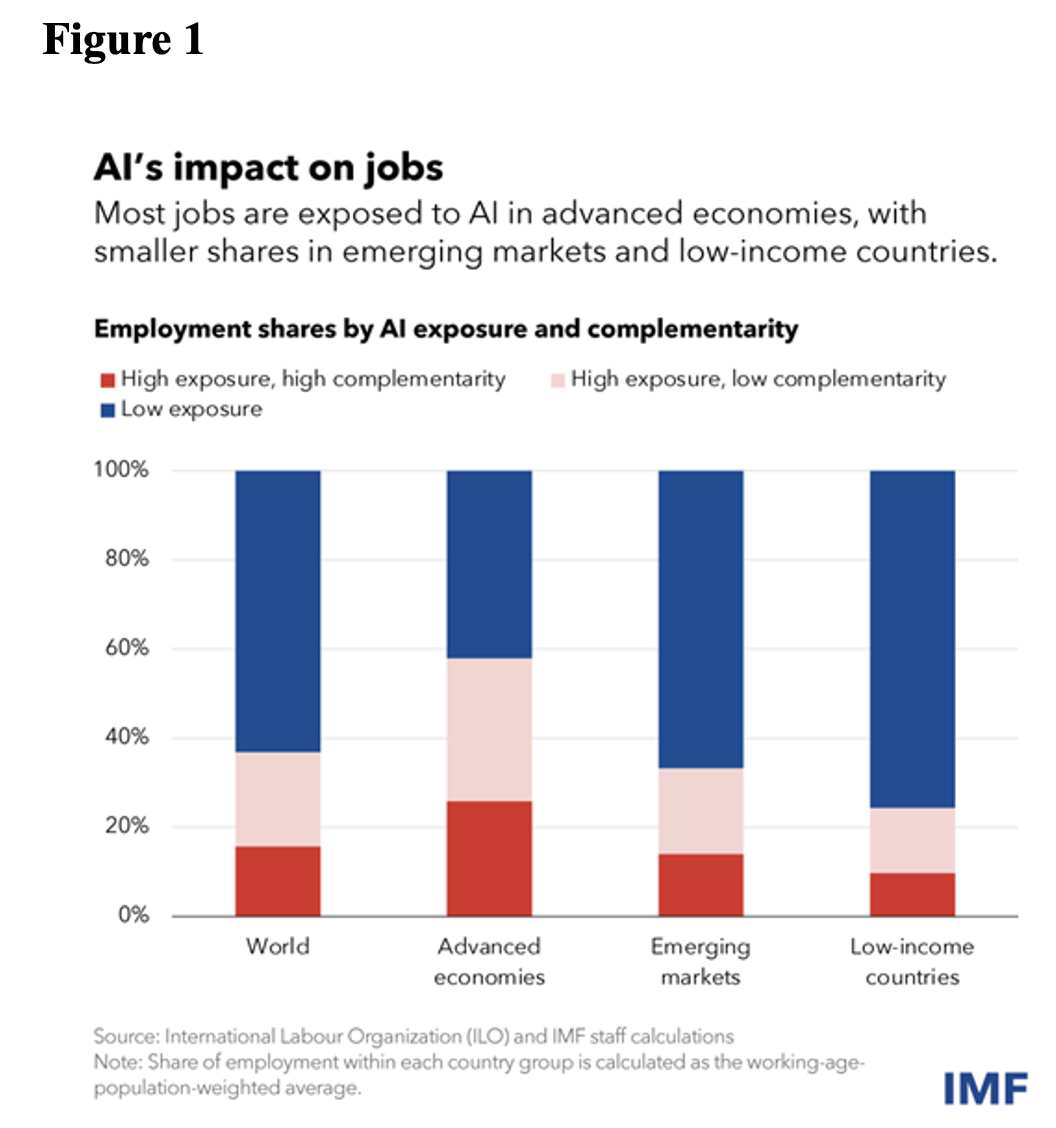
The report estimated that half of the jobs impacted will be affected negatively, while the other half may see increases in productivity. The lesser impact on emerging and developing countries will tend to lead to fewer benefits in terms of increased productivity.
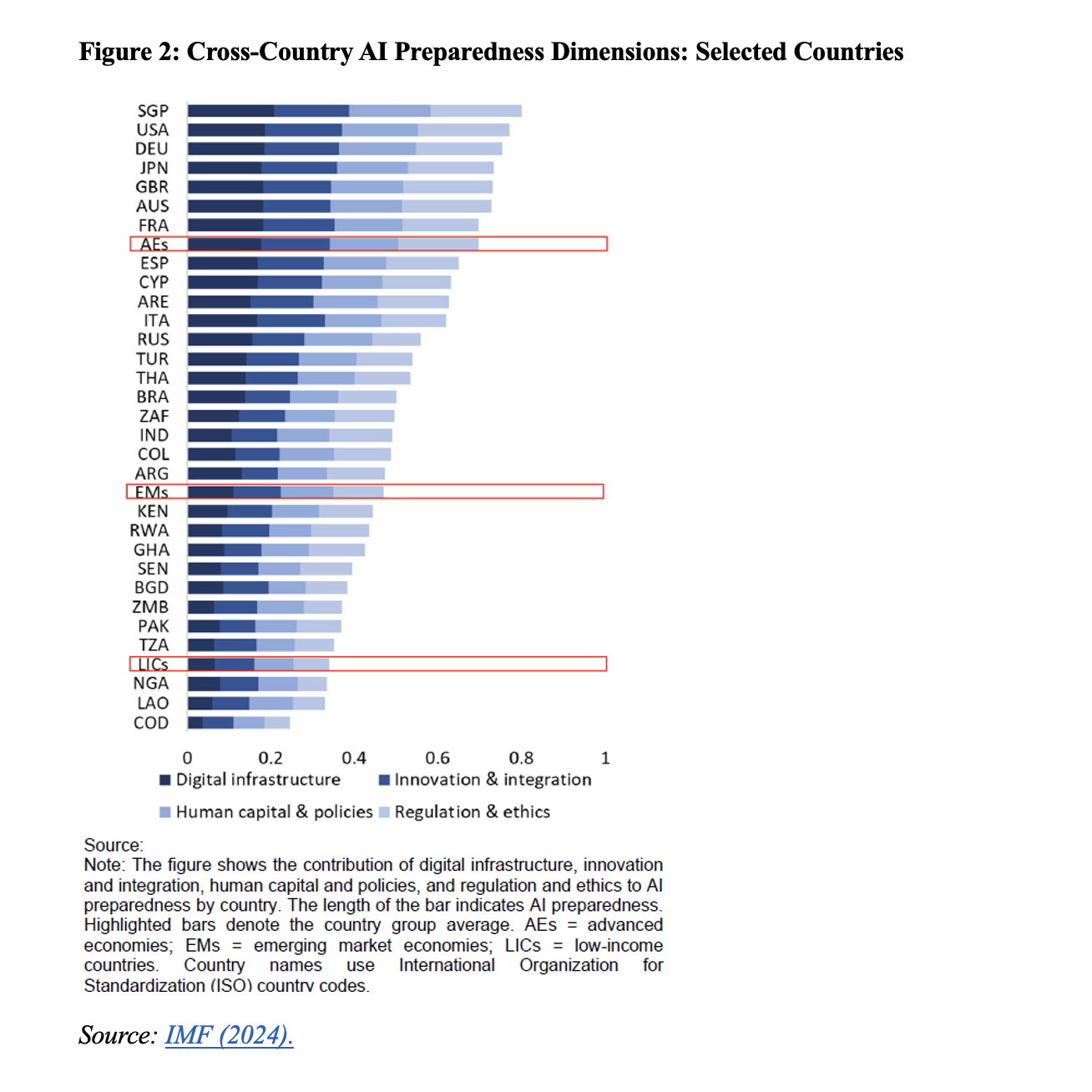
The report highlighted how a country’s level of preparedness for AI will be relevant when it comes to maximizing the benefits and dealing with the risks of the technology’s negative effects. The report included an index to measure the state of preparation of countries, taking into account digital infrastructure, economic integration and innovation, levels of human capital and labor market policies, and regulation and ethics.
In a set of 30 countries evaluated in detail, Singapore, the United States, and Germany appear in the top positions, while middle-income countries appear alongside low-income countries at the bottom (Figure 2). Increasing each country’s level of AI preparedness should clearly be considered a policy priority.