Publications /
Opinion
We finished Part I - Solving the Capital Formation Issue with a question? How should institutional investors go about looking for the best partners to help them make successful investments in Africa; and fundamentally, the real question to ask is, what are the variables required for building successful investment platforms in Africa?
Whenever one meets with an allocator from an institutional investor to discuss an allocation to an Africa strategy, the first question on their checklist is track record ? Ultimately, allocators at large institutional pools of capital, namely the pension plans, endowments and foundations, are first and foremost interested in capital preservation. The incentive structures are such that there are no prizes for taking risks, only consequences for losing capital. Therefore, when institutional investors venture into a new region/sector or new managers, they rely on their peers for support in vetting the opportunities – the point being that of a recognized investor takes the plunge, it is because thy have done the “work”. So they are “pack hunters”. Invariably what this means is what they prefer are the Blackstones, KKRs, Bains, Permiras or Doughty Hansens as managers; choices for which the institutional investor would not be criticized for selecting were the manager lose investors’ money because it is based on conventional wisdom!
In my experience speaking and working with third party marketers (firms and people who raise capital from institutional investors), institutional investors or even lay investors from more developed regions on investing Africa, they are all guilty of applying Maslow’s Hammer; or as they say of Generals in the military, they always fight the last war!
To be frank, for many investors - professional or not - Africa is not akin to anything they have seen. So they do the only thing they know and understand:
they measure it based on their current environment. Suffice to say; by that measure few investment opportunities are viable in Africa.
So the obvious question to ask is what are the drivers of returns and value creation for any private equity operation? Another way to address this issue is to look at the history of each of the firms listed above and ask what is it that all of the firms listed above have in common because when these firms started, there was no Private Equity industry the way we know it today.
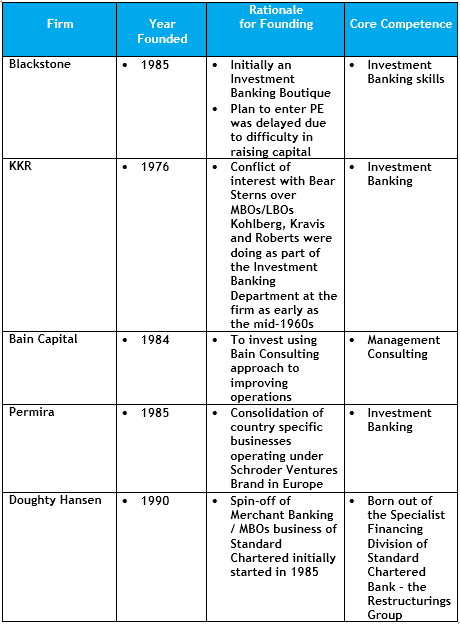
Now let us look at what are the keys to the success of this group ?
1. Buy low sell high…Valuation is the key; ultimately, in price determines returns!
- Each of these players understood valuation and knew how to value the opportunities before them. All of these players, except for Bain, come from an investment banking/restructuring background where understanding of valuation is the foundation of the business. In the case of Bain, they came to understand valuation from the operational improvement side which was the core of the work that all the people involved in Bain Capital did as consultants
2. Ability to protect themselves as an investors and incentivize people:
Protecting yourself upfront and building in the right incentives increases likelihood of success; in fact, prevent loss while retaining a call option on the upside
- Each of these players had worked on a myriad of transactions for their corporate clients. They competed on how aggressively they protected their clients – basically getting the best deal on divestitures, sales or restructurings; so when it came to doing it for their own account, they were well versed in the art
3. Network is Critical: Access to deal flow and ability to add value
- Deal flow is the life-blood of Private Equity. Each of the founders of these firms were able to develop a cross sectional view of the industries they covered working for the banks/firms they worked for. This allowed them to determine the sellers were vs not, i.e. the opportunities versus the dead ends
- This cross sectional view of industries also allowed them to compare and come to understand why one company was better than another. It also allowed them to develop relationships with the “doers”, the managers Private Equity in the US and Europe was built on resuscitating corporate orphans and underperforming/distressed businesses and fixing them
- In short, they knew where the opportunities lay, which ones were worth buying at what price and knew where to find new management to add the value need
4. Knowing how to get out: To quote Henry Kravis (Co-Founder of KKR),”…any fool can overpay and buy a company”, “…congratulate us when we sell it.”
- Having sold may companies for their clients as bankers, consultants each of these founders was intimately familiar with how to position a company for sale
- The options are selling to the players in the same industry or taking the company public; again having covered the industries to uncover the opportunity, they knew the buyers well. As bankers they had all managed divestitures and worked on IPOs
Replicating these skill sets in Africa is not as easy for the following reasons
1. Valuation; Understanding valuation in the African context is more complicated
- Issues include lack of information, fluctuating currencies and inflation,
- Valuation is a triangulation exercise and in the African context you have more variables to consider; not only does gathering the corroborating information require a local presence, but also the personnel that know how to get it
- It is important to have done it in similarly transitioning economies in other jurisdictions
2. Structuring: Comfort with the local legal systems, investor protection laws and tax efficiency issues means educating investors
- This element requires educating both the investors and target companies
- Africa has traditionally been a credit market and not an equity market.
So bringing new ways to structure agreements and getting the target companies, and the market, comfortable with the different provisions that investors will require is important to unlocking the growth
- Again experience from other changing/evolving jurisdiction is important
3. Deal flow and adding value: This is where the new entrants into the
African PE market will be most challenged
- Most of the new entrants are accustomed to using intermediaries, as they do in their home markets. Unfortunately, the intermediary market in Africa is not yet sufficiently developed; local banks and boutiques do not have the depth of experience, and in case of boutiques the critical mass, to provide the services professional investors have come to expect
- The large banks, which are the obvious intermediaries for a foreign investor, do not have an investment banking culture. They do not have the know-how, experience or the incentive structure to drive investment banking
- The best opportunities are usually not the ones being sold; these opportunities are unlikely come to market through one of these intermediaries
- Just as in Latin America when that region first came onto the world investment grid in the late 1980s/ early 1990s, investors must access targets directly (i.e. the investor knows the seller/target) or through their trusted relationships, and give birth to the deal over time
- From the perspective of adding value to portfolio companies, many investors will look to the international consulting firms to help them add value. I would actually suggest that such a approach will likely lead to failure
- The secret lies in finding local solutions…this can only be done if the investor has local relationships and understands how local businesses operate locally
- The Market for opportunities is a bifurcated one;
- There are the larger state owned enterprises that the governments are looking to privatize
- This is a restructuring exercise for the investor where it is a question of institutionalizing the operation as a private company for the benefit of its shareholders
- Then there are the smaller family owned businesses that have been operating for a generation or more that lack scale, structure, management, and often capital
- These businesses are not institution ready. Some of these businesses may even require a partner to prepare them for an institutional partner/PE investor in the US/European context
- All this is to say that US/European style PE will need to adapt to succeed in Africa
- It actually means PE firms operating in Africa will need to roll up their sleeves and invest management time in their portfolio companies more than they are accustomed to
4. Managing the exit: To be successful, the investor will probably need to manage his own exit
- As stated earlier, the Investment Banking industry in Africa is very nascent and the industry does not have the experience or reach to add value to a professional investor in a divestiture mandate
- The most important element in sell side advisory is knowing the likely buyers; at this time, the local Investment Bankers do not have these relationships; and the global Investment Banks have not yet grown sufficiently in Africa Suffice to say that there are no global PE platforms that have all these skill sets resident in the operations. The next best option is for the interested platforms to build Africa teams are fully equipped. Elements of the skills can be imported from a platform’s team(s) in other emerging jurisdictions, but it will take time build the full skill sets successfully as most of the Africans available to populate the teams with lack the requisite experience to add value at the outset. There are some Africans with the requisite skill sets, not enough to meet the need of the market. Some of them have formed firms and are operational, but they are having difficulty raising capital for the reasons articulated earlier. So it will take time for market for both people and capital to find its natural equilibrium, as it is early days yet in the life cycle of the PE industry in Africa.
The true take away for me in all of this is the following; the large PE firms core competence/know-how was actually developed and honed over time by the global Investment Banks as part of their on going investment banking services, so there was a lot of capital invested in developing this core competence that the PE firms never paid for. Now in the Africa context, the same level of investment will be required to map the landscape for companies and people and develop the core competence. The real question is does Global PE have the capital or patience to do that now that they own the industry?









