Publications /
Opinion
This brief presents an analysis of key trends and observations from the 2024 U.S. presidential election, in which I participated through the American Council of Young Political Leaders (ACYPL) Election Exchange Program, organized in collaboration with the U.S. Department of State. The program offered a comprehensive exploration of contemporary U.S. electoral dynamics, focusing on party strategies, demographic shifts, media influence, and campaign finance. The insights presented here reflect my personal observations of the evolving American electorate and do not represent the views of ACYPL or the U.S. Department of State.
1. Ideological Polarization, Partisanship, and the Tribalization of the Electorate
The 2024 U.S. election cycle underscores a significant intensification of ideological polarization, with both major parties increasingly emphasizing ideological purity. This shift aligns voter identity more closely with partisan allegiance, leading to ‘tribalized’ voting in which political support is rooted in identity affirmation rather than policy evaluation. This pattern contributes to a polarized environment with limited space for cross-party dialogue, pushing both parties toward internal homogeneity.
These dynamics are further reflected in the demographic support patterns observed in recent polling data. Across key battleground states (Arizona, Michigan, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin), the presidential race remains tightly contested, with a notable gender divide: women support Harris by a margin of 10 points (50% Harris – 40% Trump), while men lean toward Trump by 12 points (51% Trump – 39% Harris). This gender gap is evident across racial demographics. For example, Black women show strong support for Harris (net +74), and Black men exhibit a significant margin (net +43). However, Harris’s lead is less pronounced among Hispanic men (net +6), despite a higher Democratic identification (net +13).
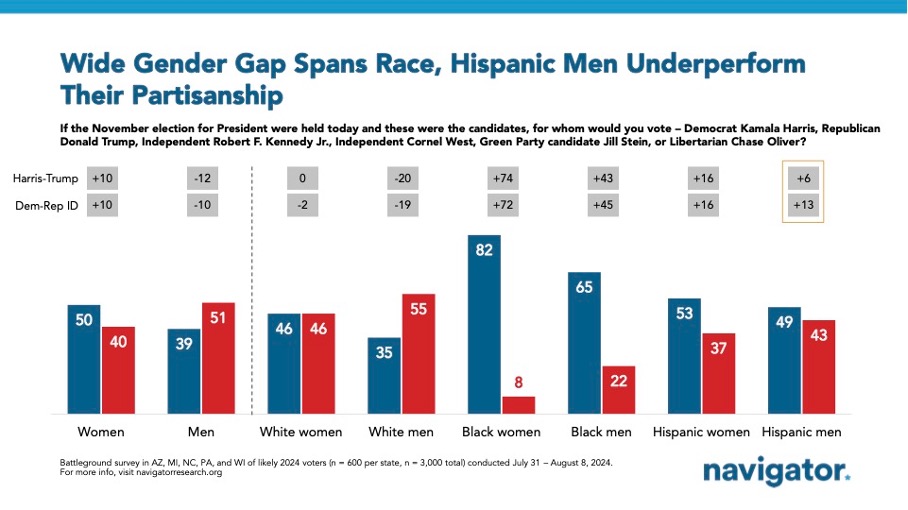
Harris’s appeal among independents remains mixed, trailing Trump by 5 points overall (38% Harris – 43% Trump – 13% third-party). The gap widens among independent men (net -19), while independent women display an even split (39% Harris – 39% Trump). These figures highlight the nuanced nature of ‘tribal’ voting across demographic lines.
2. The Decline of Policy-Centered Discourse in Electoral Campaigns
The observed shift toward emotionally resonant, identity-based appeals reflects a broader decline in policy-centered discourse within the 2024 election cycle. Campaigns increasingly prioritize mobilization over nuanced policy debate, subsuming key issues—such as immigration, healthcare, and climate policy—within partisan narratives. This focus on ideological alignment and values-based messaging has reshaped electoral success, centering it on identity alignment rather than policy specifics.
VP Harris, for instance, has garnered strong support across Democratic demographics, including Black women and young voters. Yet she faces challenges in resonating with independents, who weigh attributes such as being ‘up to the job’ and having ‘a vision’—qualities identified as critical drivers of vote choice. These attributes illustrate the importance of personal credibility over policy discussions, as candidates work to affirm their leadership capacities within the partisan expectations of their base. The result is an electorate increasingly mobilized around affective affiliations rather than informed policy positions, with party loyalty often displacing nuanced engagement with complex issues.
3. Campaign Finance and the Influence of Dark Money on Electoral Integrity
Campaign finance remains a central element in the 2024 election, with both parties reliant on substantial contributions from individual megadonors and super PACs. A Super PAC, or “independent expenditure-only committee,” is a type of political action committee in the United States that can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money to advocate for or against political candidates. Unlike traditional PACs, Super PACs cannot contribute directly to candidates or coordinate with their campaigns; instead, they operate independently, often funding advertisements and other media efforts to influence public opinion. The ability of Super PACs to accept unlimited contributions from corporations, unions, and individuals has amplified their role in U.S. elections, raising questions about transparency and the influence of wealth in political processes.
The continued influx of dark money—contributions that evade standard disclosure requirements—further highlights a trend toward financial polarization, with campaign financing structures aligning policy priorities more closely with affluent donors rather than broad-based voter interests.
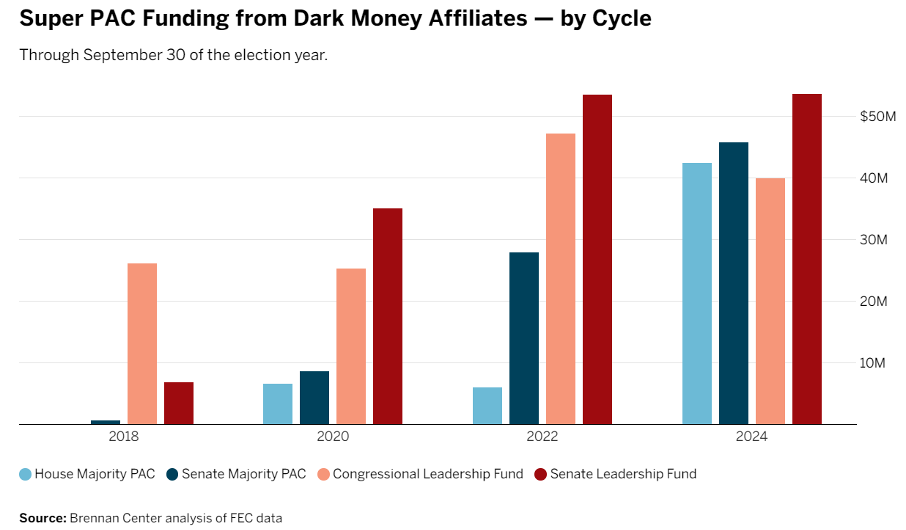
The complexities of financial influence are further compounded by the polarized partisan environment, with campaign finance strategies amplifying the divisions within the electorate. Super PACs operating with minimal transparency allow for targeted financial influence, and anonymous contributions introduce opacity in electoral accountability. As these resources increasingly shape campaign messages and policy agendas, the alignment between electoral objectives and constituent needs may grow tenuous, raising questions about the accessibility and integrity of the democratic process.
4. Shifting Demographic Strategies: Adaptation and Outreach in the 2024 Election
Both parties are recalibrating their outreach strategies to engage critical demographic groups, particularly Hispanic and Black voters, whose growing weight in the overall electorate necessitates tailored engagement. The Republican emphasis on localized engagement addresses district-specific issues to build credibility, while the Democrats focus on high voter turnout through digital platforms to mobilize younger voters, who often align with the party’s social and economic values.
Polling data reflects these strategic adaptations. Although Democrats have strong support across diverse demographics, VP Harris’s campaign still faces challenges. Harris’s overall favorability among independents is higher than that of President Biden (net -8 versus Biden’s net -16), yet she still struggles to gain traction with some segments of independent voters. Down-ballot Democratic candidates in Senate and Governor races, however, consistently outperform Harris among independents and weak Republicans (47% Democratic candidate – 43% Republican candidate), suggesting that local Democratic candidates may resonate more effectively on specific policy issues.
These demographic strategies highlight the evolving nature of political engagement within the U.S., where identity-based appeals must be balanced with targeted messaging on community-specific concerns. As parties adjust their outreach, the patterns of allegiance across key demographic groups will continue to shape electoral outcomes, influencing long-term shifts in party alignment and demographic representation.
5. Social Media’s Role in Amplifying Polarization and Shaping Public Opinion
Social media continues to be a vital tool in modern U.S. electoral campaigns, significantly influencing voter engagement and public opinion. Each party has adapted platform-specific strategies, with Republicans utilizing X (formerly Twitter) for broad-based discourse, and Democrats favoring narrative-building on platforms such as Instagram. These segmented approaches allow for direct communication with tailored audiences, reinforcing ideological messaging, while leveraging the distinct features of each platform.
However, this digital engagement also raises ethical concerns over data privacy and targeted advertising, given the absence of stringent U.S. regulations on data use in political campaigns. Such practices deepen ideological divides, as tailored content often reinforces existing biases rather than fostering balanced perspectives. In this way, social media has evolved into more than a communication tool; it is now a central influence in electoral behavior, amplifying partisanship and shaping public opinion in ways that reinforce ideological silos and limit cross-party engagement.
Conclusion
The observations drawn from the electoral exchange program I participated in reveal crucial dynamics in the 2024 U.S. presidential election, providing insights into ideological polarization, the decline of policy-focused discourse, the impact of campaign finance, demographic realignment, and the transformative role of social media. Together, these elements illustrate an electoral landscape shaped by identity affirmation, financial polarization, and segmented political communication.
As U.S. politics continue to evolve, the growing tribalization of the electorate suggests that voter behavior may increasingly align with ideological loyalty rather than policy considerations. Campaign finance trends highlight the influence of private contributions on policy priorities, while social media’s role in modern campaigns underscores its capacity to engage—and divide—the electorate. Ultimately, these patterns underscore the importance of understanding the structural shifts within American democracy as the political environment adapts to new challenges and pressures.




