Publications /
Opinion
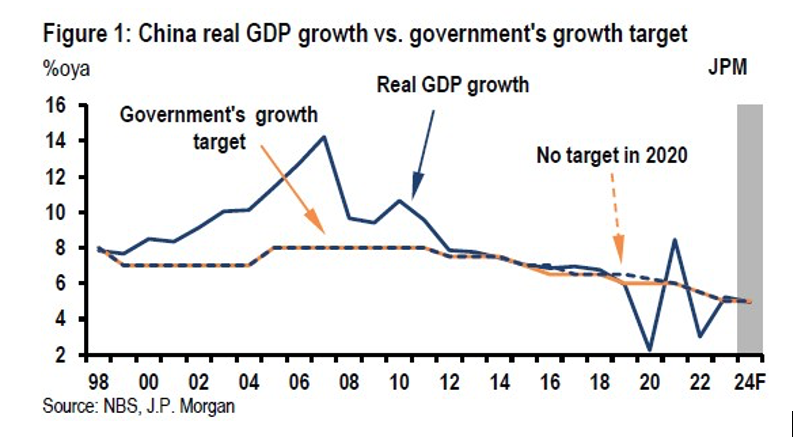
The Internaional Monetary Fund World Economic Outlook, issued on April 16, projected China’s economic growth rate at 4.6% and 4.1% for, respectively, 2024 and 2025. In 2023, after China’s economic reopening with the end of the ‘zero-COVID’ policy, the rate was 5.2%, above the official target of 5% (Figure 1).
For 2024, the official target has been set at 5% again. Notwithstanding the challenges we discuss here, China’s macroeconomic performance in the first quarter of 2024 has been in sync with the official target (He et al, 2024).
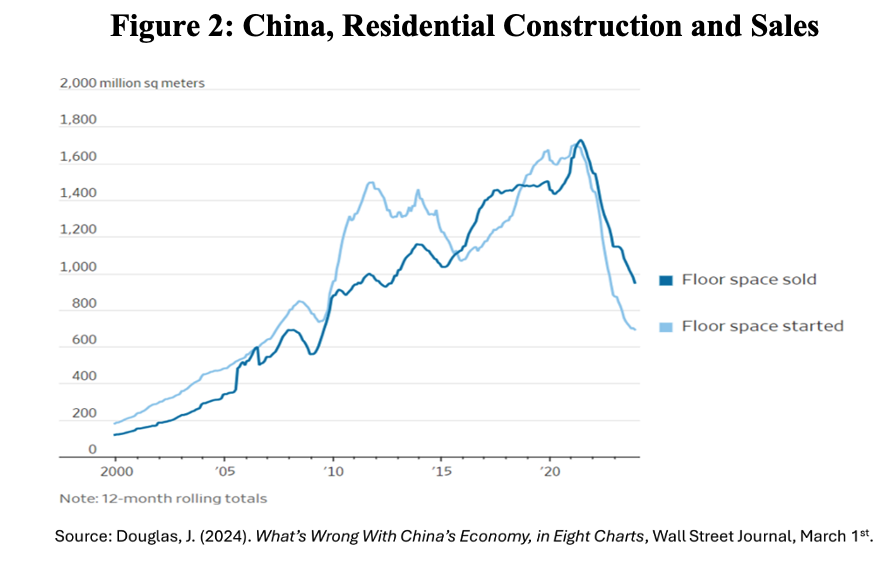
Six headwinds affecting China’s economic growth in the coming years can be identified. The first is the exhaustion of the real-estate sector as a growth factor, after having grown to a quarter of the country’s GDP. Restrictions put in place in 2021 by the Chinese government on access to cheap credit for developers because of concerns about the size of the real estate bubble, have not only cut the boom, but have also exposed the fragility of developers’ assets, as highlighted by the collapse of developer Evergrande. Since then, there has been a sharp drop in home sales, new construction, and investment in the sector (Figure 2).
Local government debt is another problem, especially because local government revenues from land sales to real-estate developers have shrunk. The degree of exposure of Chinese banks to both real estate and local government, with possible consequences in terms of loan defaults, could negatively affect the supply of credit to the economy.
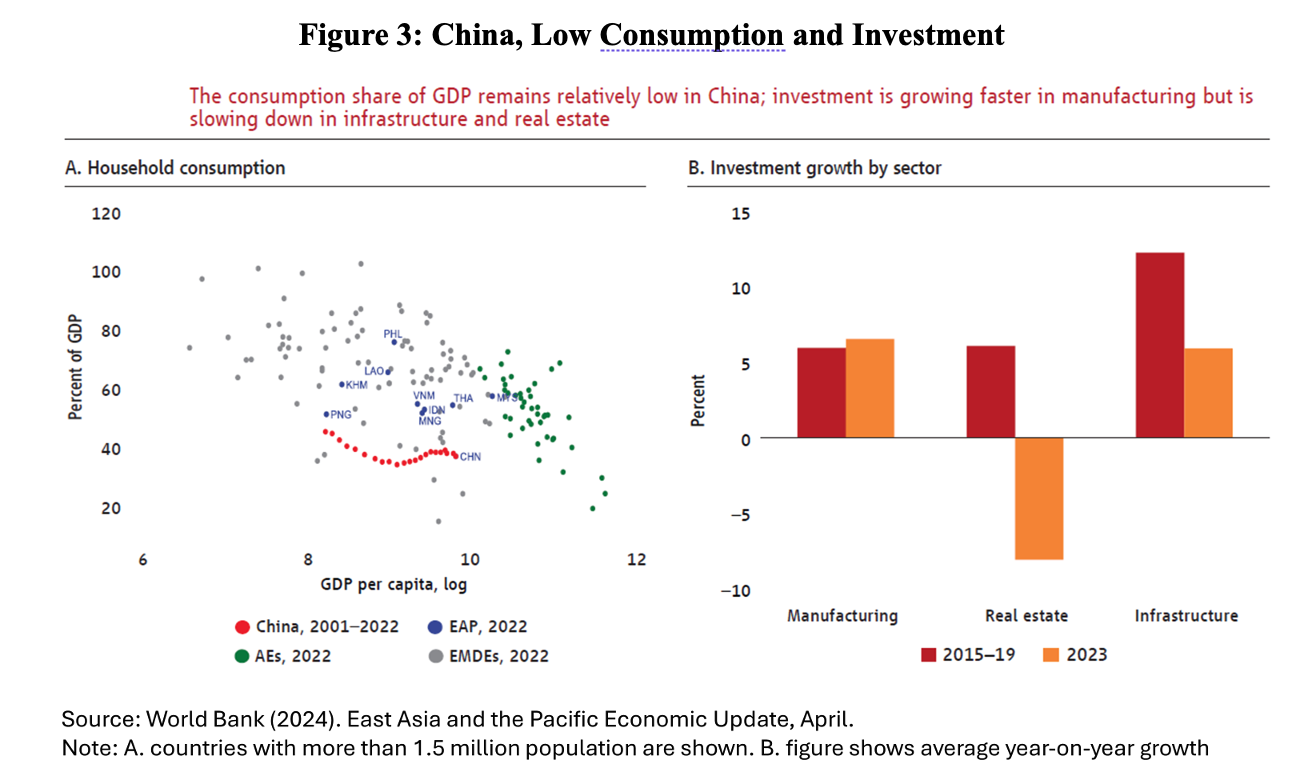
The third challenge for growth is a problem with domestic demand by households. Chinese households took on heavy debt to buy real estate during the boom, and spending cuts accompanied the housing turbulence. Even though it increased after the end of Zero-COVID last year, domestic consumption remains on a lower trajectory than before the pandemic. Measures of consumer confidence point to this. Reduced private investment in the domestic market, as well as reduced hiring, have accompanied this retrenchment by domestic consumers.
What about the external sector as a form of compensation? A fourth challenge to Chinese growth lies in external resistance to such an increase in exports as an alternative, given that they now face resistance that has built up in the wake of the intensification of geopolitical rivalry abroad, especially in relation to the U.S. and other advanced economies.
The Chinese lead in clean-energy technology has, in fact, been accompanied by a strong expansion, for example, in sales of electric cars abroad. Chinese passenger-car exports have surpassed Japan’s, at the same time as Chinese companies are seeking to strengthen positions abroad—such as BYD in Brazil, Hungary, and elsewhere. But the risks of facing additional market-access restrictions are high.
A fifth challenge concerns the radical change in the mood of foreign investors. Since the third quarter of 2023, China’s balance of payments has recorded a net outflow of almost $12 billion in direct investment, because of asset sales or non-reinvestment of profits. Portfolio investment, that is shares and debt securities, has also changed from positive to negative.
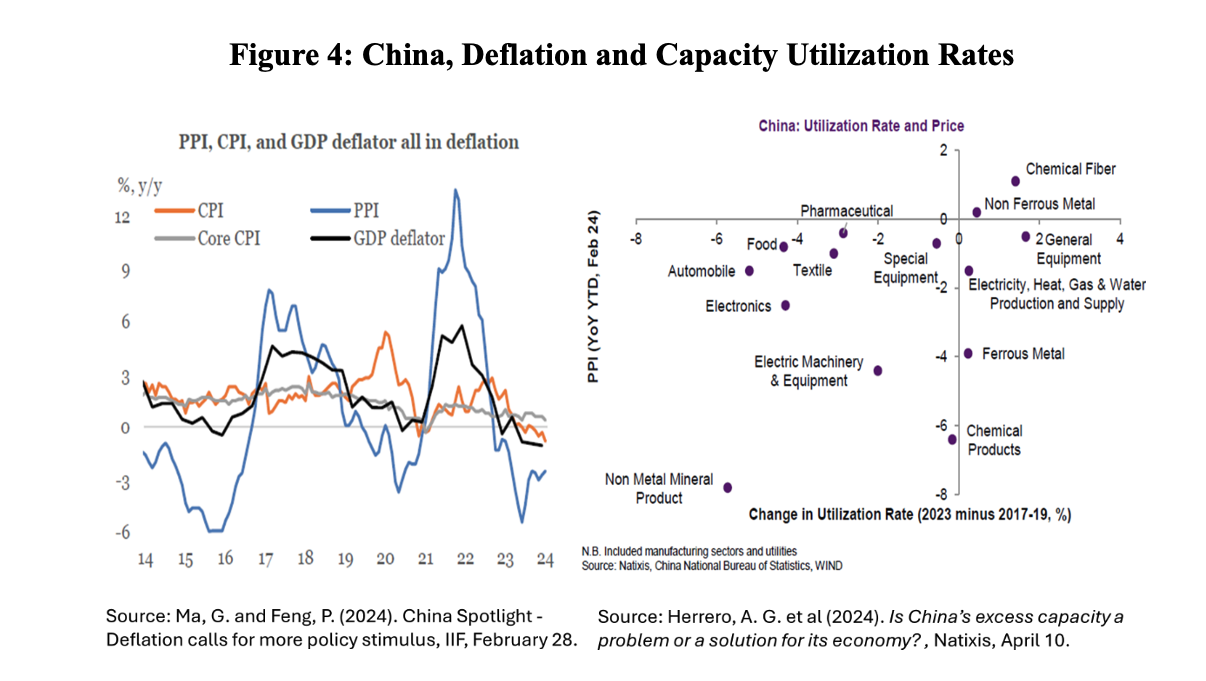
The insufficiency of aggregate demand in China is manifested as deflation in the domestic economy. Consumer prices have been stable or falling for months, and companies have been reducing prices for more than a year (Figure 4, left panel). Idle capacity is high in many sectors, reflecting the excess investments relative to levels of demand (Figure 4, right panel).
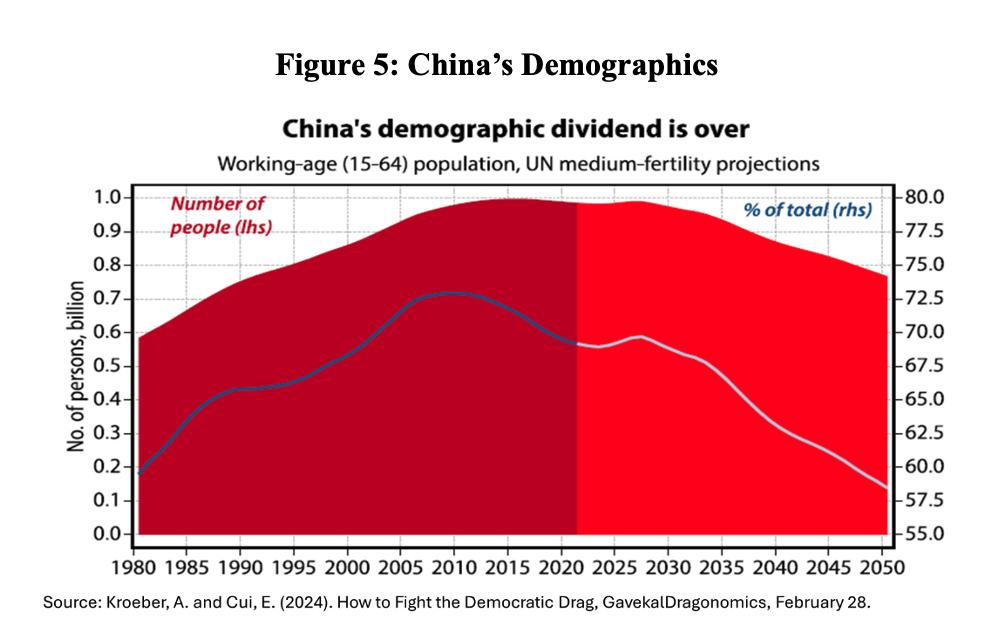
Demography is the sixth challenge. The increase in the supply of workers accompanying rapid urbanization has reached its limits. The long-term decline in the number of births and the ongoing population decline, with a growing share of the population out of the job market, means—as in many other parts of the world—the end of the demographic dividend (Andrade and Canuto, 2024) (Figure 5). The currently high youth unemployment rate means there are workers who can be employed, but this does not change the direction on the trend, or the proportion of Chinese people of non-productive age.
To understand how the first four challenges above intertwine, it is worth going back to the beginning of the last decade. In December 2011, when I was a World Bank vice president, I was at a ceremony in Beijing in which then-president Hu Jintao made one of the first statements about the need for an inevitable “rebalancing” of the Chinese economy. There would have to be a gradual redirection towards a new growth pattern, he said, no longer associated with investment rates close to 50% of GDP, or with domestic consumption increasing in relation to investments and exports.
Also, Hu Jintao said, an effort would be needed to consolidate local insertion in the highest rungs of the added-value ladder in global value chains, something that was effectively sought. Services should also increase their weight in GDP in relation to manufacturing. There would no longer be the double-digit GDP growth rates of previous decades, but growth would no longer be, as then-premier Wen Jiabao said in 2007, “unstable, unbalanced, uncoordinated, and unsustainable”.
Given the low level of domestic consumption in GDP (a fact that is still present) and, therefore, the dependence on investments and trade balances, the transition would run the risk of experiencing an abrupt drop in the pace of growth. To allay fears of an abrupt slowdown, waves of credit-driven overinvestment in infrastructure and housing followed in later years. A second round was implemented in 2015–2017, in response to a housing slowdown and stock market decline. In addition, of course, expansion policies were adopted during the pandemic crisis in 2020.
In effect, the decline in Chinese GDP growth rates occurred only gradually to 6% in 2019. Now, however, the lever of overinvestment in real estate and infrastructure is running out, not only because of the debt levels that accompanied its extensive use, but also because, at the margin, its returns in terms of GDP growth represented a declining contribution.
Two reforms would have a strong effect on growth (Canuto, 2022). First, social protection should be reinforced to convince Chinese people to save less. Furthermore, the proposal made by Hu Jintao in 2011—and left aside by Xi Jinping—to “rebalance” public and private companies should be revived, with a consequent gain in productivity because of the differences favorable to the latter shown where they operate together.
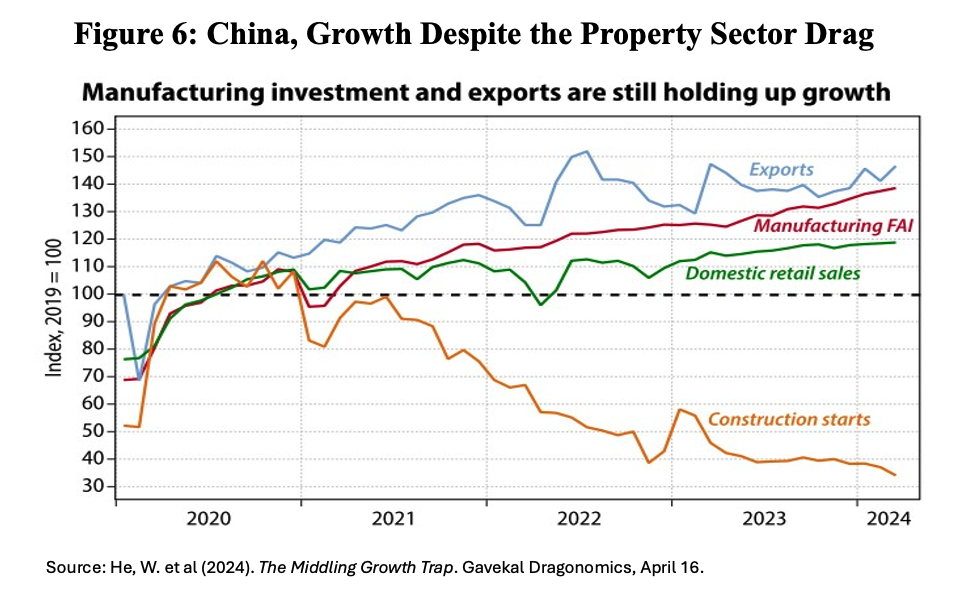
Such reforms do not seem to be on the horizon. However, despite the challenges outlined here, China’s economic growth path remained steady in the first quarter of 2024. Exports, manufacturing investment, and travel-related consumer spending compensated for the drag from the property sector (Figure 6), so far increasing the chances of achieving the target of “around 5%” GDP growth this year (He et al, 2024).